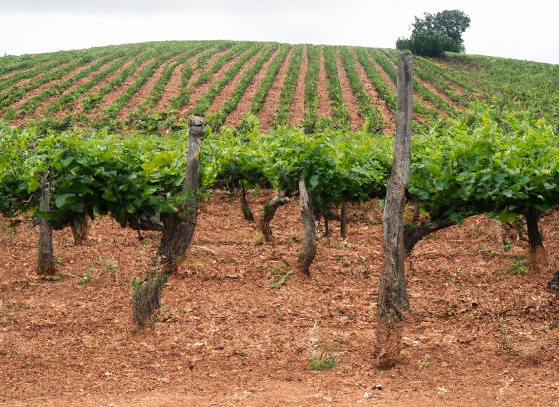
The Ebro River Valley
The Ebro (987 km / 580 miles) is the longest river in Spain.
It starts at Fontibre, flows through the limestones of central Ebro valley, and discharges in the Ebro delta on the Mediterranean Sea.
The Ebro River has carved out (between Sierra Cantábrica and Sierra Demandaout the most famous Spanish vineyards: Rioja DOCa, Cariñena DO and Calatayud DO.
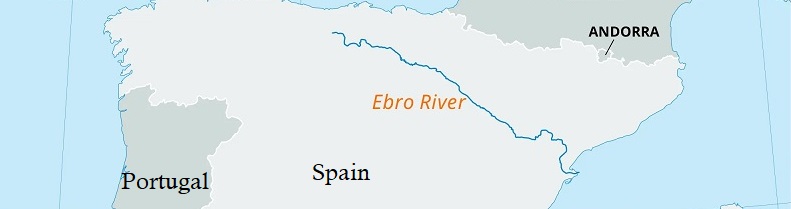
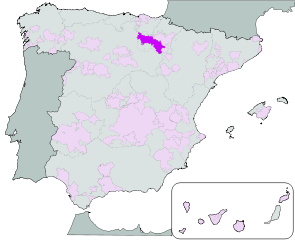
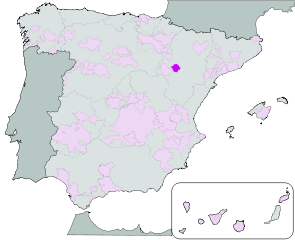
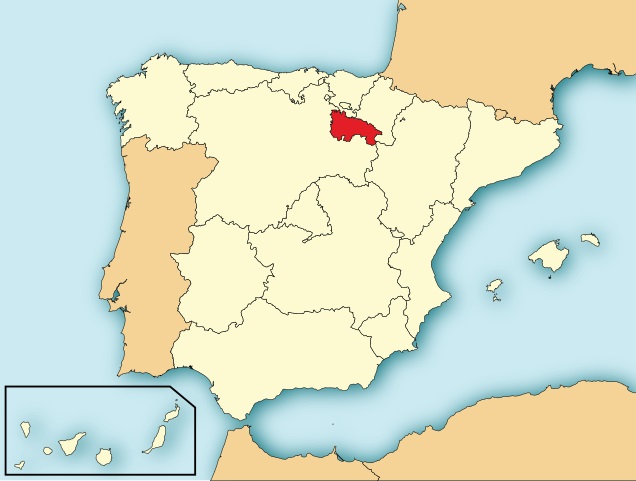
Wine Region Rioja
Rioja is a famous wine region in the north-central part of Spain. It is Spain’s largest red wine producing region with over 600 wineries and an annual production of over 400 million bottles.
The Rioja region is a denominación de origen calificada, "Qualified Designation of Origin (D.O.Ca)", the highest category in Spanish wine regulation.
Rioja wines ares made from grapes grown in La Rioja and Navarre, and the Basque province of Álava.
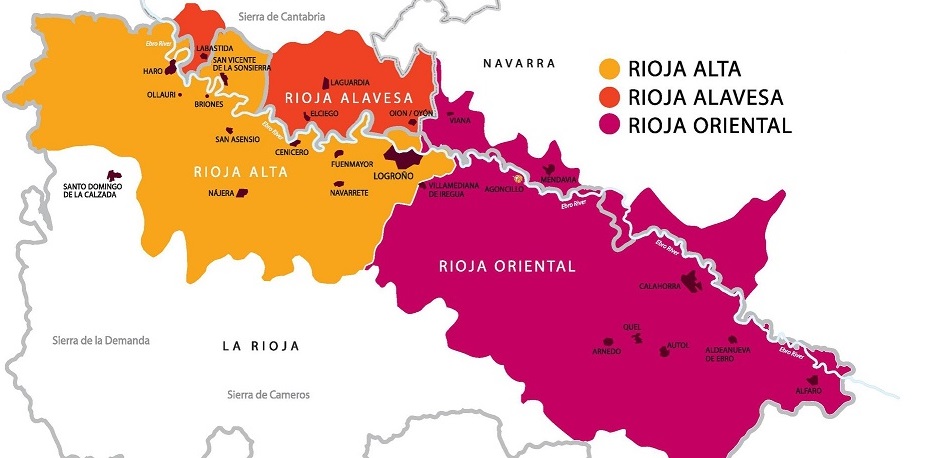
The key appellations are Rioja Alta, Rioja Alavesa, and Rioja Oriental (previously Rioja Baja).
Rioja Alta (Rioja High)
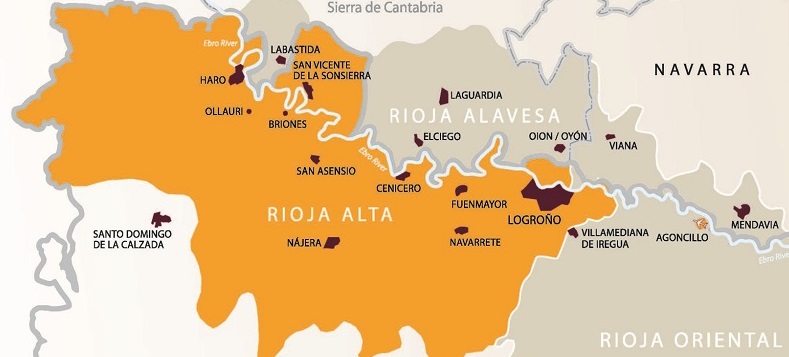
Rioja Alta is Located on the western side of Rioja. It has an Atlantic climate, and its soils consist of iron-rich clay mixed with limestone. Thanks to the elevation and cooler temperatures, Rioja Alta wines have more tannin and higher acidity than Rioja Oriental, and they are often more elegant.
Rioja Alavesa
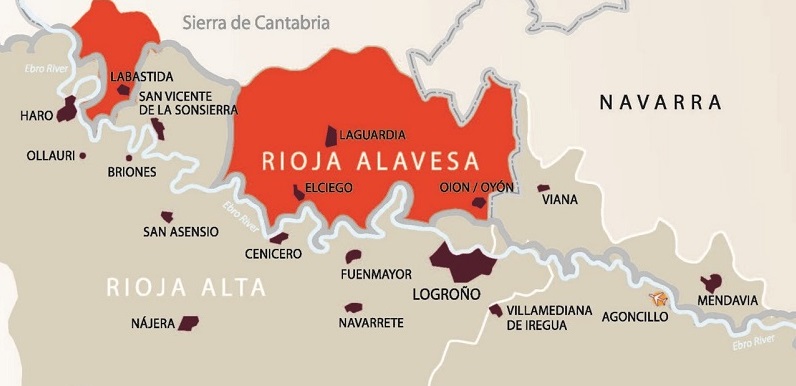
Rioja Alavesa is the smallest of the Rioja regions. It is located between the Ebro River and the rocky mass of the Sierra Cantabria. The wines bear a high resemblance to the wines of Rioja Alta with high tannins and high acidity.
The vineyards here are located at high altitudes, resulting in cooler temperatures that aid in the acquisition acid levels and good colour. The soil is rich in chalky clay, limestone and sand.
Rioja Oriental (Rioja East)
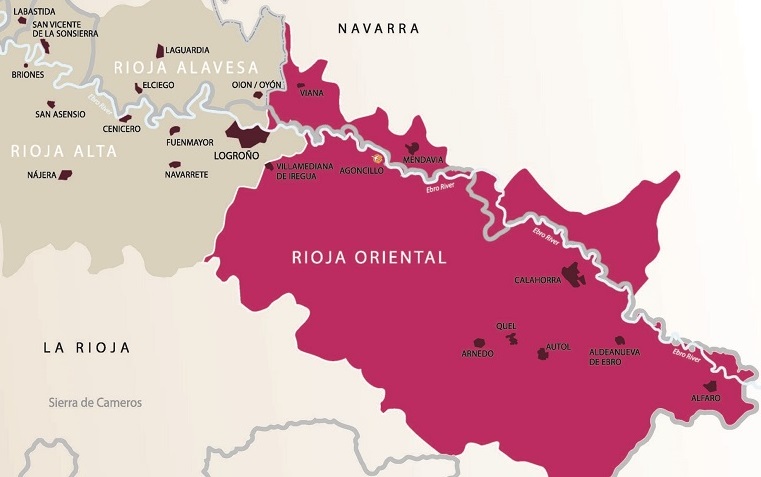
The wines from Rioja Oriental (Rioja East), formerly the Rioja Baja (Rioja Low) are fruit-forward and the wineries focus on wines designed to drink young.
Red Wines
The region is best known for high-quality Rioja Wines.
A typical Rioja blend consists of 60% Tempranillo ("the Grape of Spain") and 20% Garnacha along with other fruity additives like Mazuelo (Cariñena) and Graciano.
White Wines
Viura (Macabeo) is the dominant white grape in Rioja, accounting for 70% of white varieties.
Viura is also found in France, particularly in Roussillon and the Languedoc, where it is called Maccabeo or Maccabeu.
Nine white varieties is allowed to use in white Rioja: Viura, Malvasía Riojana, Garnacha Blanca, Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, Verdejo, Maturana Blanca, Tempranillo Blanco and Torrontés.
DOCa Rioja (La Rioja)
Rioja was the first Spanish wine region to obtain DO status in 1925. In 1991, it was promoted to DOCa (Qualified Designation of Origin), a higher category reserved for wines maintaining a proven consistency and quality over a long period of time.
| Black Grapes | White Grapes |
|
88% Tempranillo |
70% Viura (Macabeo) |
| Red Wines | White Wines |
|
|
Viura (Macabeo) |
| Soil | Climate |
|
Rioja Alta: Rioja Alavesa:
Rioja Oriental (Baja): |
Hilly Riverbanks. |

Cariñena DO (Aragon)
Cariñena is the largest and oldest DO in Aragon (1932).
It has given its name to the the Cariñena grape.
Cariñena is called Mazuelo elsewhere in Spain and Carignan in France.
| Black Grapes | White Grapes |
|
32% Garnacha Tinta |
3% Macabeo |
| Soil | Climate |
|
Poor Gravelly Soil. |
Hot and Dry. Continental. |

Poor Cariñena soil on gravels from the Sistema Ibérico mountains.
Calatayud DO (Aragon)
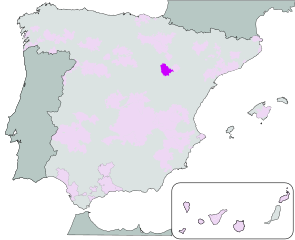
Calatayud achieved DO status in 1990. It is Aragon’s second largest DO region after Cariñena.
Pricipal Reds
Garnacha Tinta, Tempranillo, Syrah, Bobal, Monastrell.
Pricipal Whites
Macabeo, Garnacha Blanca, Malvasía and Chardonnay.
Climate
Altitude: 800m.
Soil: Grey and red slate, limestone, clay and loam, gypsum and pebbles.
Campo de Borja DO (Aragon)
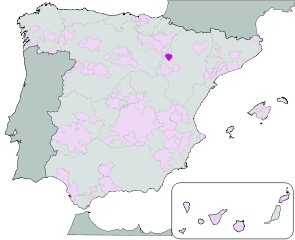
Campo de Borja achieved DO status in 1990.
Pricipal Reds
Garnacha Tinta, Tempranillo, Syrah, Mazuela, Cabernet, Merlot.
Pricipal Whites
Macabeo, Moscatel, Chardonnay, Garnacha Blanca, Sauvignon Blanc and Verdejo.
Climate
Altitude: 350 - 750m.
Soil: Brown clay, stony in terraces and limestone-ferrous..
Alcohol can be addictive. Always drink in moderation.
© Copyright 2015-2025 W3 Wine School. All Rights Reserved.