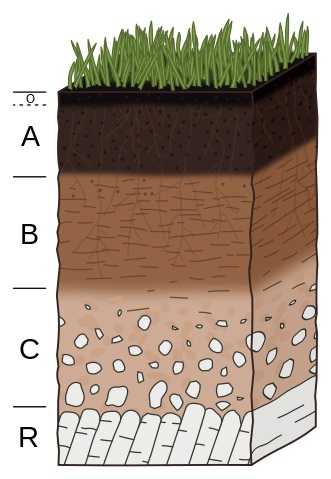
What are Soils?
Soil is the "Skin of the Earth". It is the loose, upper layer of earth in which plants grow.
Soil Supports Plant Life and is vital to life on earth.
Soil is a mix of organic material, clay, silt, sand and rock particles laying on top of the bedrock:
- Minerals. Sand, Silt and Clay from weathered Rocks.
- Water. Fills pore Spaces, holds dissolved Nutrients.
- Air. Fills pore Spaces. Essential for Organisms.
- Living Organisms. Bacteria, Fungi, Insects, Roots.
- Remains Dead Organisms.
Soil Textures
Soil Texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in the soil.
The texture determines the soil's crucial properties:
- Drainage
- Water Retention
- Aeration
- Fertility
- Workability
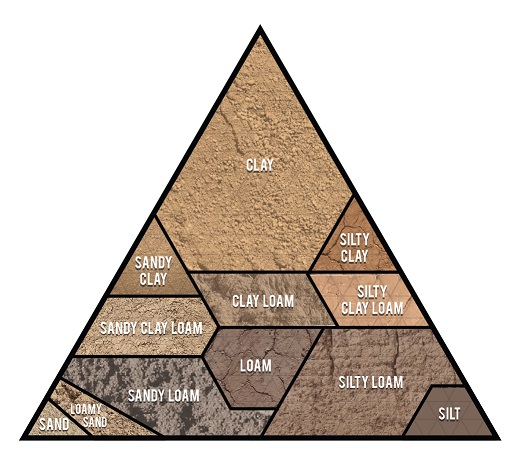
Image from USDA Natural Resources Conservation
| Texture | Clay | Slit | Sand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | 80% | 10% | 10% |
| Sandy Clay | 50% | 0% | 50% |
| Silty Clay | 50% | 50% | 0% |
| Loam | 20% | 40% | 40% |
| Silty Loam | 20% | 70% | 10% |
| Sandy Loam | 20% | 10% | 70% |
| Silt | 10% | 80% | 10% |
| Sand | 10% | 10% | 80% |
Soil Particles
Scientists have classified soil particles into the groups: Clay, Silt, Sand, Gravel and Pebbles.
| Name | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Clay | Very small particles, < 0.002 mm. Formed by weathering and erotion of rocks. |
Tend to pack so water cannot drain and air cannot penetrate. |
| Silt | Medium sized rock dust, 0.002-0.050 mm. Formed on the bottom of water bodies. |
Fertile. Water retaining. Between sand and clay. |
| Sand | Larger particles, 0.050-2 mm. Formed from broken rocks and minerals. |
Mineral rich. Retains heat. Holds little water but allows good aeration. |
| Gravel | Small, rounded stones, 2-4 mm, often mixed with sand | Good drainage. Retains heat. Infertile. Poor water retention. |
| Pebbles | Rounded stones 4 - 64 mm, found on beaches and in rivers. | Great drainage. Retains heat. Infertile. Noor water retention |
Clay

Wet Clay

Red Clay

Dry Clay
Clay soils have the finest particles and are known for their water retention capacity.
Clay soils contain more than 30 percent fine clay particles. Some clays swell and shrink as they wet and dry, which can add to soil fertility.
Clay soils take longer to warm up in spring. Wet clay soils are easily damaged when dug or walked on.
Drought is much less damaging on clay soils than others soil types.
Pros:
- Holds water and nutrients the longest of all soil types
- Less susceptible to drought
Cons:
- Prone to compaction
- Callenging for root penetration
- Poor drainage
Silt

Silty soils have medium-sized particles, smaller than sand, larger than clay.
Pros:
- Fertile
- Water retaining
- Less susceptible to drought
Cons:
- Poor drainage
- Prone to contration
- Similar to clay
Sand

Pure Sand

Coarse Sand

Loamy Sand
Sand is a granular material composed of mineral particles smaller than gravel and coarser than silt.
Sand warms up quickly in the spring, aiding early vine growth, but can dry out quickly.
Pros:
- Great drainage
- Mineral Rich
- Heat retaining
- Phylloxera free
Cons:
- Poor fertility
- Susceptible to drought
Gravel



Gravel are aggregates of more or less rounded rock fragments coarser than sand.
Pros:
- Good drainage
- Retains heat
Cons:
- Infertile
- Poor water retention
Pebbles

Pebbles are small stones made smooth and round by the action of water or sand.
Pros:
- Great drainage
- Retains heat
Cons:
- Infertile
- Roots have to dig deep to find nutrients
- No water retention
Alcohol can be addictive. Always drink in moderation.
© Copyright 2015-2025 W3 Wine School. All Rights Reserved.